[ad_1]
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured what scientists consider is probably the most distant identified galaxy, after observing what astronomers name a “Cosmic Dawn” for the previous two years.
NASA stated in a press launch {that a} “Cosmic Dawn” is the interval within the first few hundred million years after the massive bang, when the primary galaxies had been born.
The galaxies, NASA stated, give scientists perception into how gasoline, stars and black holes modified when the universe was in its infancy.
A staff of worldwide astronomers used the Webb telescope in October 2023 and January 2024 to watch galaxies as a part of the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JAMES) program.
POWERFUL WEBB TELESCOPE SPIES SPECTACULAR STAR BIRTH CLUSTER BEYOND THE MILKY WAY
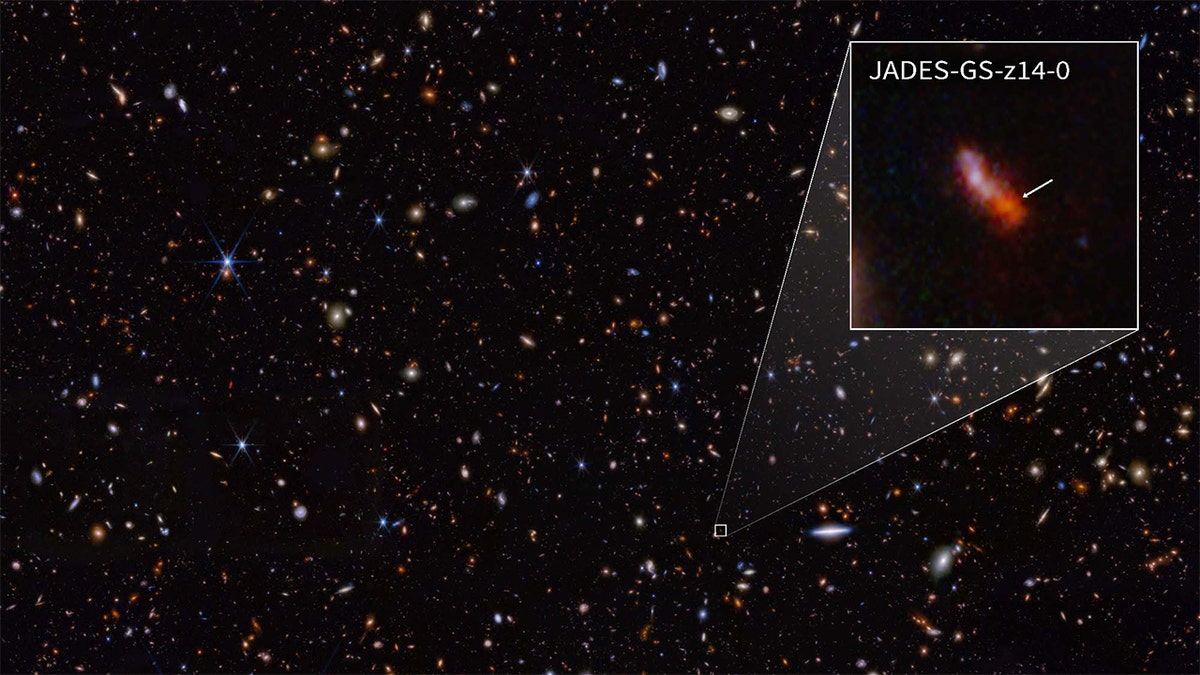

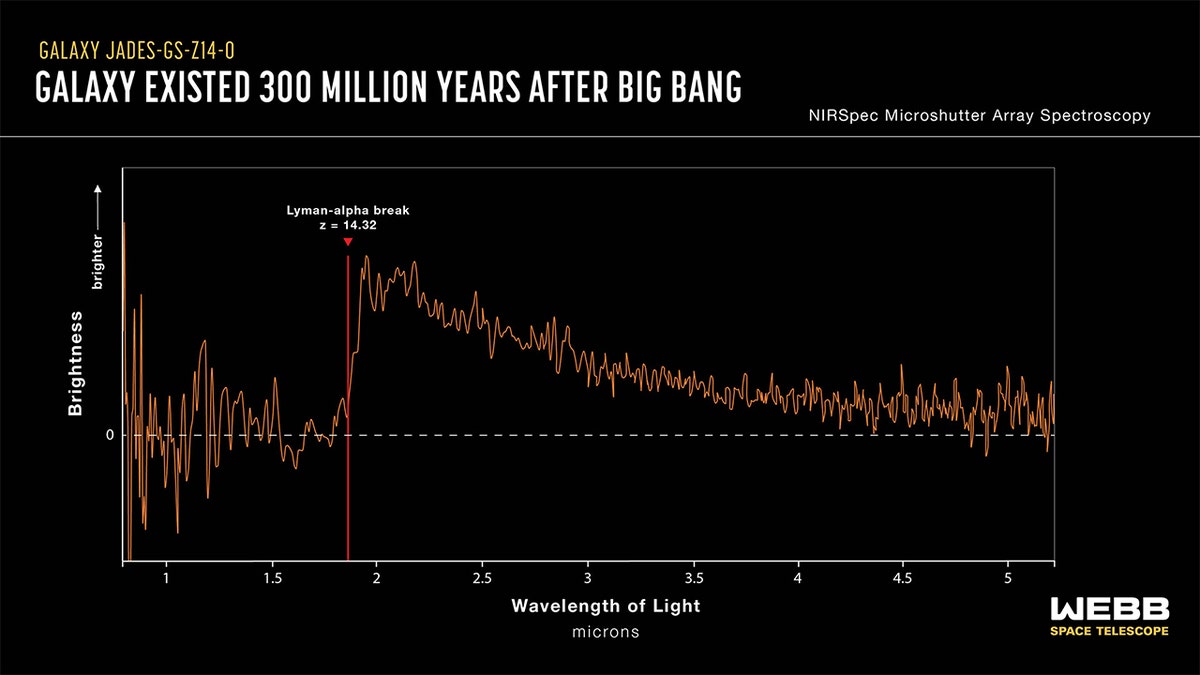
Scientists used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph) to acquire a spectrum of the distant galaxy JADES-GS-z14-0 with a view to precisely measure its redshift and subsequently decide its age. The redshift could be decided from the placement of a crucial wavelength referred to as the Lyman-alpha break. This galaxy dates again to lower than 300 million years after the massive bang. (Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, J. Olmsted (STScI). Science: S. Carniani (Scuola Normale Superiore), JADES Collaboration.)
During that interval, the staff collected the spectrum of what NASA known as a record-breaking galaxy, solely 290 million years after the massive bang.
The spectrum was measured by how a lot a galaxy’s gentle is stretched by the enlargement of the universe, and within the case of probably the most distant galaxy identified, it was measured with a redshift of about 14.
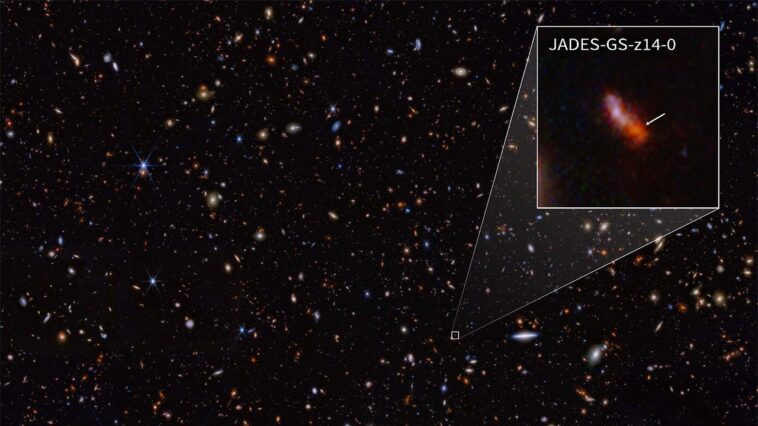
Two of the astronomers on the staff, Stefano Carniani from Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, Italy, and Kevin Hainline from the University of Arizona in Tucson, Arizona, informed NASA that in January 2024, Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) noticed the galaxy identified to astronomers as JADES-GS-z14-0, for practically 10 hours.
MERGER OF MASSIVE BLACK HOLES FROM EARLY UNIVERSE UNCOVERED BY WEBB TELESCOPE, SCIENTISTS SAY
The NIRCam knowledge was used to find out which galaxies to check additional with spectroscopic observations. One such galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0 (proven within the pullout), was decided to be at a redshift of 14.32 (+0.08/-0.20), making it the present record-holder for probably the most distant identified galaxy. This corresponds to a time lower than 300 million years after the massive bang. (Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, J. Olmsted (STScI). Science: S. Carniani (Scuola Normale Superiore), JADES Collaboration.)
When the spectrum first processed, the astronomers stated, there was unambiguous proof the galaxy had a redshift of 14.32, which might shatter the most-distant galaxy document of 13.2, held by JADES-GS-z13-0.
The discovery of the spectrum was “incredibly exciting” for your complete staff due to the thriller surrounding the supply. They additionally stated a very powerful facet of the galaxy was how luminous the galaxy was from such a far distance.
The galaxy is estimated to be greater than 1,600 gentle years throughout, and the sunshine is suspected to be coming from younger stars and never emission from a rising supermassive black gap.
WITNESS THE MESMERIZING CONJUNCTION OF THE MOON AND VENUS IN SPACE
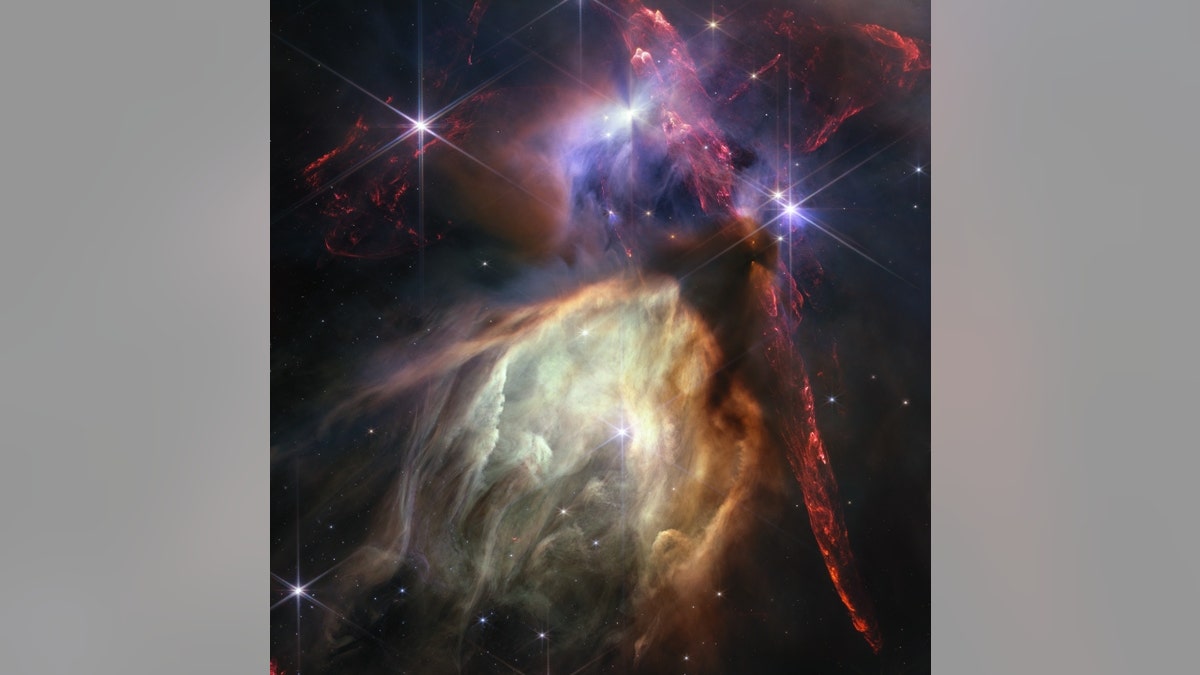

The first anniversary picture from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope shows star start prefer it’s by no means been seen earlier than, filled with detailed, impressionistic texture. The topic is the Rho Ophiuchi cloud advanced, the closest star-forming area to Earth. It is a comparatively small, quiet stellar nursery, however you’d by no means understand it from Webb’s chaotic close-up. Jets bursting from younger stars crisscross the picture, impacting the encircling interstellar gasoline and lighting up molecular hydrogen, proven in purple. Some stars show the telltale shadow of a circumstellar disk, the makings of future planetary techniques. (Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Klaus Pontoppidan (STScI))
The starlight additionally implies the galaxy is a number of lots of of thousands and thousands of instances the mass of the Sun, the astronomers declare, resulting in extra mysteries of the way it could make such a shiny and big galaxy in lower than 300 million years.
The astronomers realized by means of the info that the colour of the galaxy was reddened by mud and was not as blue because it could possibly be in early phases of the galaxy.
Wavelengths of sunshine collected by Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) indicated the brightness of the supply was above what could be extrapolated from the measurements of different devices on the telescope, suggesting the presence of ionized gasoline emission from hydrogen and oxygen.
They say oxygen being current at such an early stage suggests a number of generations of large stars already lived their lives earlier than the telescope was in a position to observe the galaxy, the astronomers stated.
“All of these observations, together, tell us that JADES-GS-z14-0 is not like the types of galaxies that have been predicted by theoretical models and computer simulations to exist in the very early universe,” the astronomers stated within the press launch. “Given the observed brightness of the source, we can forecast how it might grow over cosmic time, and so far, we have not found any suitable analogs from the hundreds of other galaxies we’ve observed at high redshift in our survey.
“It is probably going that astronomers will discover many such luminous galaxies, probably at even earlier instances, over the following decade with Webb,” the team added. “We’re thrilled to see the extraordinary range of galaxies that existed at Cosmic Dawn!”
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FRESH NEWS APP
The findings are still being studied and have not been through the peer-review process, according to NASA.
The Webb Telescope, the successor to the Hubble and the largest telescope ever launched into space, is a joint project of NASA and the European Space Agency.
[ad_2]
Source link



