Internal linking plays a pivotal role in the architecture of a website, both in terms of user experience (UX) and search engine optimization (SEO). When implemented effectively, it can significantly boost your website’s search engine ranking, improve content discoverability, and create a seamless user navigation experience. In this chapter, we’ll dive deep into the concept of internal linking, how it impacts SEO, and best practices for building a logical site hierarchy.
What is Internal Linking?
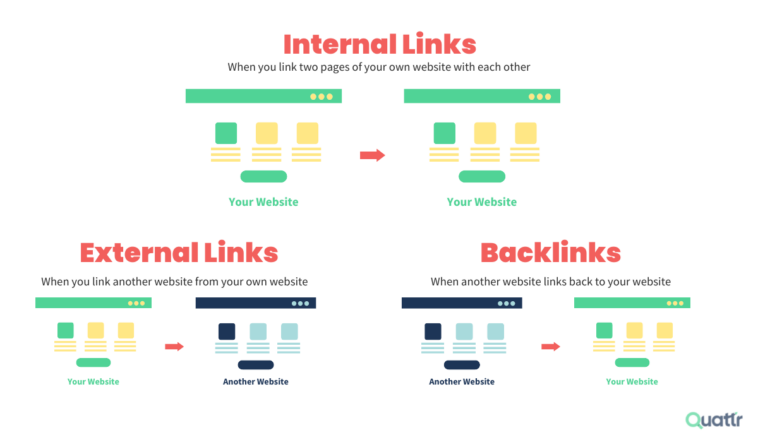
Internal linking refers to hyperlinks that connect one page of a website to another within the same domain. These links serve as the pathways through which both search engine crawlers and users navigate a site. Internal links are crucial for several reasons:
- SEO: They help distribute link equity (or “link juice”) throughout the site, signaling to search engines which pages are most important.
- User Experience: They guide users to relevant content, ensuring they don’t get lost while browsing your site.
- Content Discoverability: Internal links help search engines find and index new pages, boosting your site’s visibility.
Why is a Logical Site Hierarchy Important?
A logical site hierarchy is fundamental for both internal linking and SEO. The site hierarchy refers to the way in which content is structured across the site, from the homepage down to individual posts or product pages. An organized hierarchy ensures that content is easy to find, both for users and search engines.
Benefits of a Logical Site Hierarchy:
- Improved Crawlability: Search engine bots follow internal links to crawl pages and index content. A clear hierarchy makes it easier for search engines to access and index all important pages.
- Enhanced User Experience: Users can navigate a well-organized website intuitively, finding relevant content with minimal effort.
- Link Equity Distribution: A well-planned hierarchy ensures that link equity is passed effectively from high-authority pages (like the homepage) to other important pages on the site.
Key Elements of a Logical Site Hierarchy
- Flat vs. Deep Structure: A flat structure minimizes the number of clicks needed to reach any given page, which improves usability. A deep structure, on the other hand, requires users (and search engines) to click through multiple layers of pages. A shallow or flat structure is often preferred for better user experience and faster indexation.
- Categories and Subcategories: Grouping related pages into categories and subcategories helps to organize content in a meaningful way. Categories provide a top-level structure, while subcategories further break down content into more specific topics.
- URL Structure: URLs should reflect the site hierarchy. For example:
- Homepage: example.com
- Category Page: example.com/category
- Subcategory Page: example.com/category/subcategory
- Product or Post: example.com/category/subcategory/product
A URL that mirrors the content’s position within the site hierarchy is user-friendly and helps with SEO by providing clear indications of content relevance and structure.
How Internal Linking Affects SEO
Internal linking plays a critical role in how search engines assess the importance of various pages on your site. Let’s break down the key ways internal linking can impact SEO:
- Distributing Link Equity (Link Juice):
- When one page links to another, it passes on some of its authority (link equity) to the linked page. The homepage typically carries the most authority, and internal links from this page help distribute that authority throughout the site.
- This distribution of link equity ensures that pages deeper in the site hierarchy receive the attention they deserve from search engines, boosting their chances of ranking in search results.
- Anchor Text Optimization:
- Anchor text refers to the clickable text in a hyperlink. Using descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text helps search engines understand the content of the linked page.
- Properly optimized anchor text for internal links can enhance the relevance of your pages in relation to specific search queries.
- Improved Crawl Efficiency:
- Search engine crawlers follow internal links to discover new pages. A clear internal linking strategy makes it easier for crawlers to find and index all important pages, ensuring they don’t miss key content.
- Using a site structure with proper internal linking makes sure that deep pages aren’t isolated (or orphaned), ensuring they get the indexing they deserve.
- Dwell Time and Bounce Rate:
- By guiding users through relevant pages, internal links increase the likelihood that visitors will stay on your site longer, reducing bounce rates. Lower bounce rates and higher dwell times are positive ranking factors for SEO.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
- Plan Your Site Hierarchy:
- Before you start linking, it’s essential to map out your site’s architecture. Determine your main categories and subcategories, and decide how content will flow from the homepage down to specific posts or product pages.
- Ensure the most important pages are no more than 2-3 clicks away from the homepage. This will facilitate a flat structure that’s easy to navigate for both users and search engines.
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text:
- Always use descriptive, relevant, and natural-sounding anchor text for your internal links. Avoid overstuffing anchor text with exact-match keywords, as this can appear spammy and negatively affect SEO.
- Example: Instead of “Click here”, use something like “Read more about content marketing strategies” if linking to a relevant post.
- Link to Relevant Pages:
- Internal links should always be relevant to the content you’re linking to. This not only benefits SEO but also enhances the user experience by guiding visitors to related content.
- For instance, if you write a blog post about SEO best practices, link to your in-depth SEO guides or product pages on SEO tools.
- Maintain a Logical Flow:
- Ensure that internal links follow a logical structure and are contextually relevant. For example, don’t link to unrelated content just because you want to increase internal links.
- Ideally, each internal link should make sense to both the reader and the search engine in terms of the overall topic flow.
- Use Breadcrumbs:
- Breadcrumb navigation is a great way to help users and search engines understand the structure of a site. Breadcrumbs provide a clickable path back to higher-level pages (e.g., Home > Category > Subcategory), helping with both navigation and SEO.
- Monitor and Update Broken Links:
- Over time, pages on your site may be removed or moved. Regularly check for broken internal links, as they can harm the user experience and SEO. Tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider can help you identify and fix these issues.
- Optimize for Mobile:
- With the majority of web traffic coming from mobile devices, ensure that your internal linking is optimized for mobile users. This means ensuring that your internal links are easy to click on mobile and that they don’t clutter the page.
Final Thoughts
Internal linking is a cornerstone of a well-structured website that benefits both SEO and user experience. By establishing a clear and logical site hierarchy, using descriptive anchor text, and regularly auditing your links, you can ensure that both search engines and users can easily navigate your site. This, in turn, will help you improve your rankings, enhance content discoverability, and create a more enjoyable browsing experience for your audience. Through a strategic internal linking approach, you can build a solid foundation for SEO success and long-term growth.